The conversation about “Web Science” is becoming more urgent and more central to the future of the planet and the way we live a life worth living.



The conversation about “Web Science” is becoming more urgent and more central to the future of the planet and the way we live a life worth living.

In today’s world of climate denial and vaccine skepticism, one would be forgiven for assuming that an anti-intellectual, anti-expertise, anti-truth wave is sweeping the globe, and that the rise of the far right necessarily spells an end for science-informed policy.

At Brave Conversations we tried to do something different — not to have a conventional conference where everyone hid behind their professional personae, delivered papers and were generally spoken at.
Licensing of Engineering Professionals: Is there any validity to this practice? The Education Department of the State of New York says — there is. IEEE Policy also says there is. The reality, I have come to continuously over four decades in practice as an electrical power engineer in the service of more than a dozen U.S. firms — is that there is none!
We need our brains to adapt advantageously for ingenious design and development, especially as the time between stimulus and response becomes precariously pressurized.

Using biometric technology to identify and monitor people raises human rights concerns. In particular, biometrics are often associated with intrusions into privacy.

The next generation of socio-technical system can be seen as a kind of “focal point” for the convergence of a number of current trends in computing, information systems, and information technology. These trends include the technology-driven instrumentation of infrastructure by ubiquitous computing and/or “intelligent” devices, with the prefix “smart” now taking precedence over the prefix “e-,” i.e. SmartGrids, SmartCities, SmartMotorways, etc., rather than the e-commerce. e-health, e-learning initiatives commonplace at the turn of millennium.

Pillar 2 is focused on professional and research ethics, ethics in the development of technologies, ethics in the context of Sustainable Development and Humanitarian Technology, as well as engineering ethics education.

Mining has had an impact on many Aboriginal communities in Australia. As we move to a mining sector where dump trucks, underground excavators, loaders, and conveyor systems are transformed into partial or fully autonomous systems, there is little or no human labor required other than to maintain equipment or provide oversight using a range of distant surveillance technologies.

There is an unshakable faith in our industry that we can do anything and that everything we do must be good and beneficial to society. Our industry has had similar crises before, such as dot-com busts, that exposed our assumptions, but the ideas are still here. As an industry and society, can we continue to develop solutions that unduly amplify human behavior – so that we provide and support a way for harm to be normalized? As an industry and society, can we continue to promote solutions based on long-held and dominate theories – so that the wider community is misled by influential advocates? The answer is a clear “no” to both.

In 1997 Eduardo Kac became the first human to implant himself with a non-medical device in the performance art work titled “Time Capsule”

IEEE Technology and Society Magazine Editor-in-Chief Katina Michael has been recognized with SSIT’s highest award for service with the Brian M. O’Connell… Read More

The effect of technologies on our lives might be less about technology and more about the priorities and parameters we set.

There is an increasing interest in, and implementation of the Internet of Things. As the number and types of interconnections… Read More

A new archive of material added a new historical dimension to our discussions of cybernetics at the 2016 Norbert Wiener Conference in Australia.

Arthur Winston addressed to attendees of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Norbert Wiener in the 21st Century, Melbourne, Australia, held… Read More

Graeme Clark is the inventor of the cochlear implant. He was the dinner Keynote Speaker at the 2016 Conference on… Read More

Many stroke survivors retain some degree of paralysis and thus have limited use of their body. According to published surveys,… Read More

The future as depicted in works of science fiction, especially of the multiplex variety, is almost uniformly dystopian. The bleakness… Read More
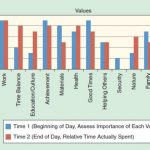
What are your values? I’m asking you, the reader. As a quick exercise, try to write down ten values you… Read More